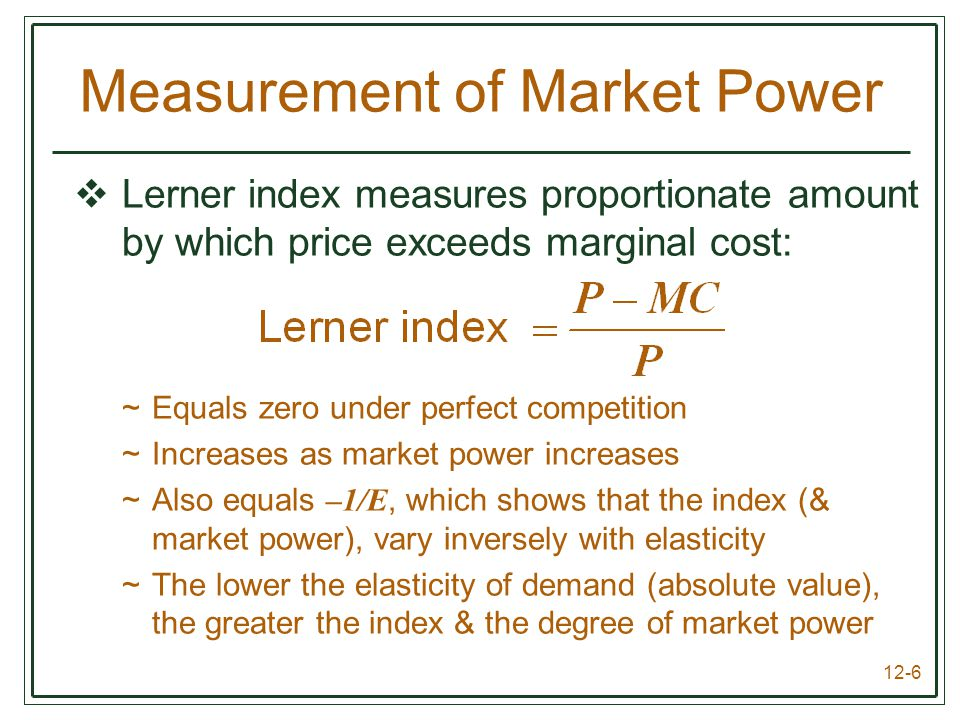
Question 1

| Market Type | Perfect Competition | Monopolistic Competition | Oligopoly | Monopoly |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Firms | Numerous | Many | Few | One |
| Nature of Product | Same, or very similar products Example: Produce |
Different products (Might seem the same but are still different) Example: Fast food restaurants |
Can be similar or different Example: Washing machines |
Unique in nature Example: Electricity |
| Implications for demand curve | Horizontal: This firm is a price taker and the demand curve is perfectly elastic |
Downward Sloping: Relatively Elastic |
Downward Sloping: Price curve is price-elastic. Demand curve is directly affected by competition |
Downward sloping: Firms in this market have the most control over price |
| Average size | Small | Small - Medium | Large | Very Large |
| Possible consumer demand | Demand is potentially unlimited. Demand will rely on what is available through supply | Demand will depend on what differentiation the competition provides | Consumers are in control of what and how to buy | Firms only produce when demand is elastic. If the product is not desirable demand will be low |
| Profit making possibility | In the short run, it's possible to make an economic profit. In the long run it's impossible for this market type to earn an economic profit |
In the short run it is possible to make a profit however in the long run there will be zero economic profit | There is potential for moderate economic profit, however how much will depend on the competition and competitive advantage over these firms. | Because firms in this industry are usually a one-of, the profit making possibility is large |
| Government intervention | Very little limitations | Very little, regulations depend on industry (eg. Food permits) | Government will monitor to ensure that Cartels and Collusions aren't manipulating the market | The government can/will impose taxes specific to the industry or profits being made. If a monopoly refuses to pay these fee's they can be shut down by the government |
| Specific trait to market | Buyers can easily switch between sellers with little to no difference in product and price | Brand loyalty aids the firm when prices are raised to increase revenue | Firms often form a collusion to stabilize markets and reduce risks. This can be highly illegal and is monitored by the government | Firms who operate as a Monopoly are one-of in their area. They have control of their market |
Question 10
The MC curve intersects the ATC curve at the minimum point of the ATC curve
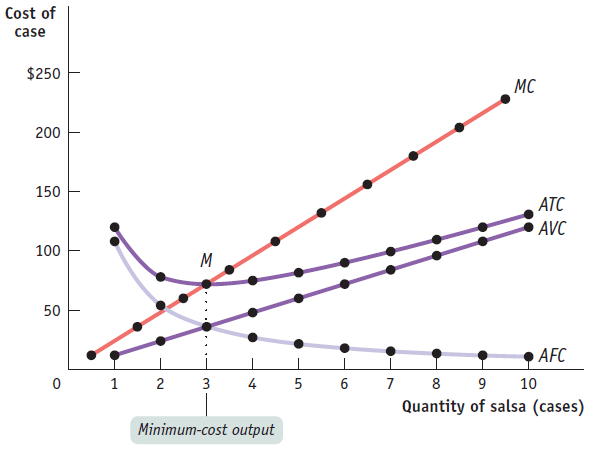
Question 11
When a new computerized system for a firm increases the marginal productivity of its workers, the marginal revenue product curve will shift to the right, causing the wage rate to increase.
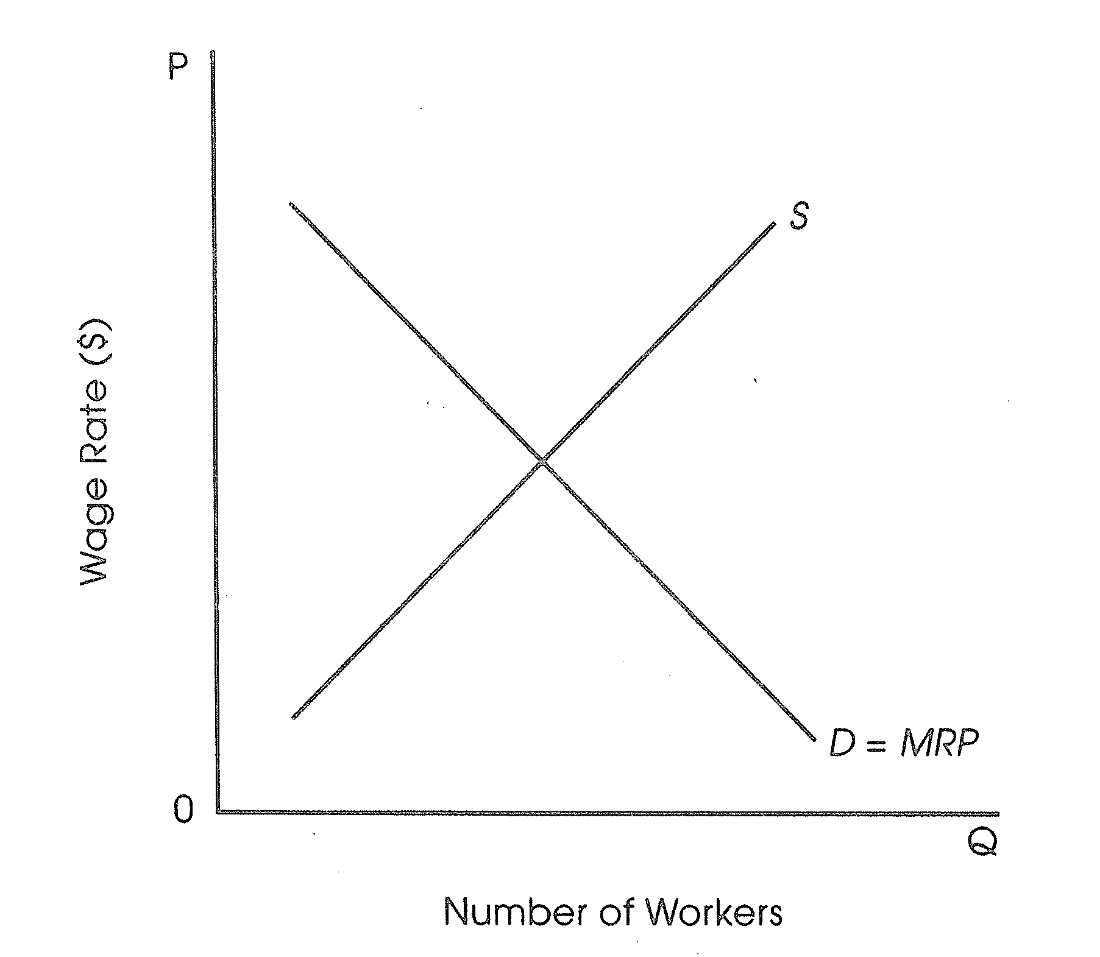
Question 14
- A consumer surplus is established as the difference between the total utility (satisfaction) received and the price paid by the consumer.
Question 19
Profits of an unregulated monopolist: difference between ATC (NOT MC) and D times the Quantity
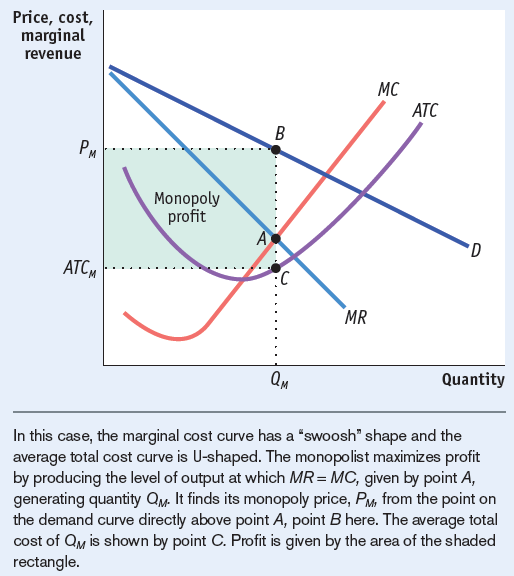
Question 23
If price < ATC, this would result in a loss

Question 24
- The government announcement would result in an increase in demand for red grape juice. But the change will not be a change along a demand curve or a change in quantity demanded.
Question 29
Source of wage differentials
Marginal Productivity and Wage Inequality
Compensating differentials
Differences in talent
Quantity of human capital
Market Power
Efficiency wage
Discrimination
Question 38
- Monopolistic competition is characterized by lower output, higher price than competitive industries. Price is greater than MR and greater than MC
Question 43

Question 49
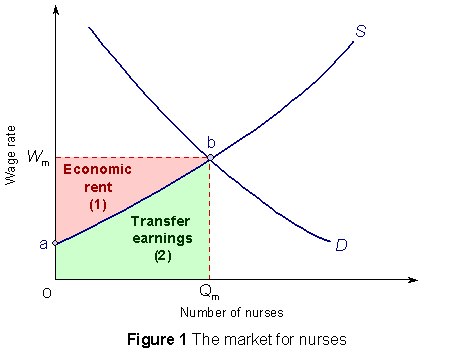
If we pay these costs including the value of what could be earned elsewhere with the same resources, we would be paying a transfer earning (the value of alternative use of the resources of suppliers).
The transfer earning is the minimum price we must pay, as consumers, in order to assure a continuing supply of goods and services.
Rents are those payments that suppliers receive that are in excess of transfer earning or are in excess of what those suppliers could earn elsewhere.
These rents cause a reallocation resources away from more productive use of resources.
Question 54
This refers to the interdependence characteristic of oligopoly.
Price decreases are matched in the hope of maintaining or increasing market share.
Price increases are not matched for fear of losing market share or having the possibility of gaining market share over the price-increasing rival
Question 55
collusive
- adj. acting together in secret toward a fraudulent or illegal end
kinked demand curve
- This curve illustrates the interdependence of rivals under non-collusive oligopoly in which rivals match price decreases but do not match price increase of an oligopolist
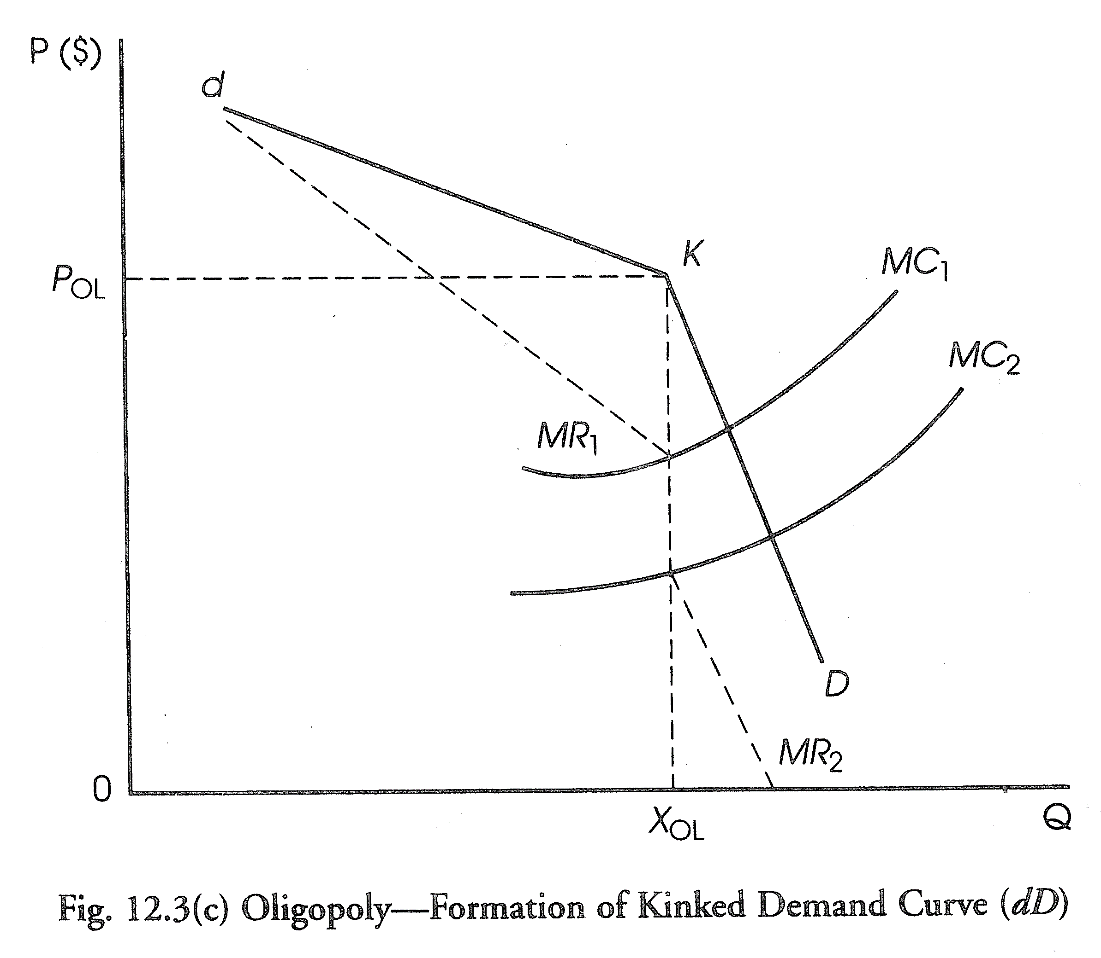
The major feature of the kinked demand curve is that it consists of two segments (one that indicates "following" and the other that "does not follow" the price changes of rivals)
Question 56
Elasticity tends to be greater in the long run since the firm will be able to adjust to changes in demand.
The firm will have more options in availability of resources in order to substitute less expensive resources (inputs) for more expensive resources in the long run
Question 58